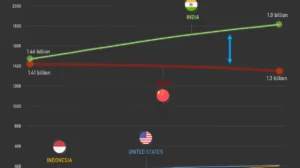
The world’s 10 most populous nations collectively have a population of approximately 4.64 billion individuals. These nations are home to more than 60% of the world’s total population, which is about 8 billion people. Additionally, six of these ten nations, such as India, China, Indonesia, Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Russia, are located in Asia. India became the world’s most populated nation in 2023 after surpassing China. In contrast, China, which had the largest population for decades, is now experiencing a decline in population.
Key Takeaways
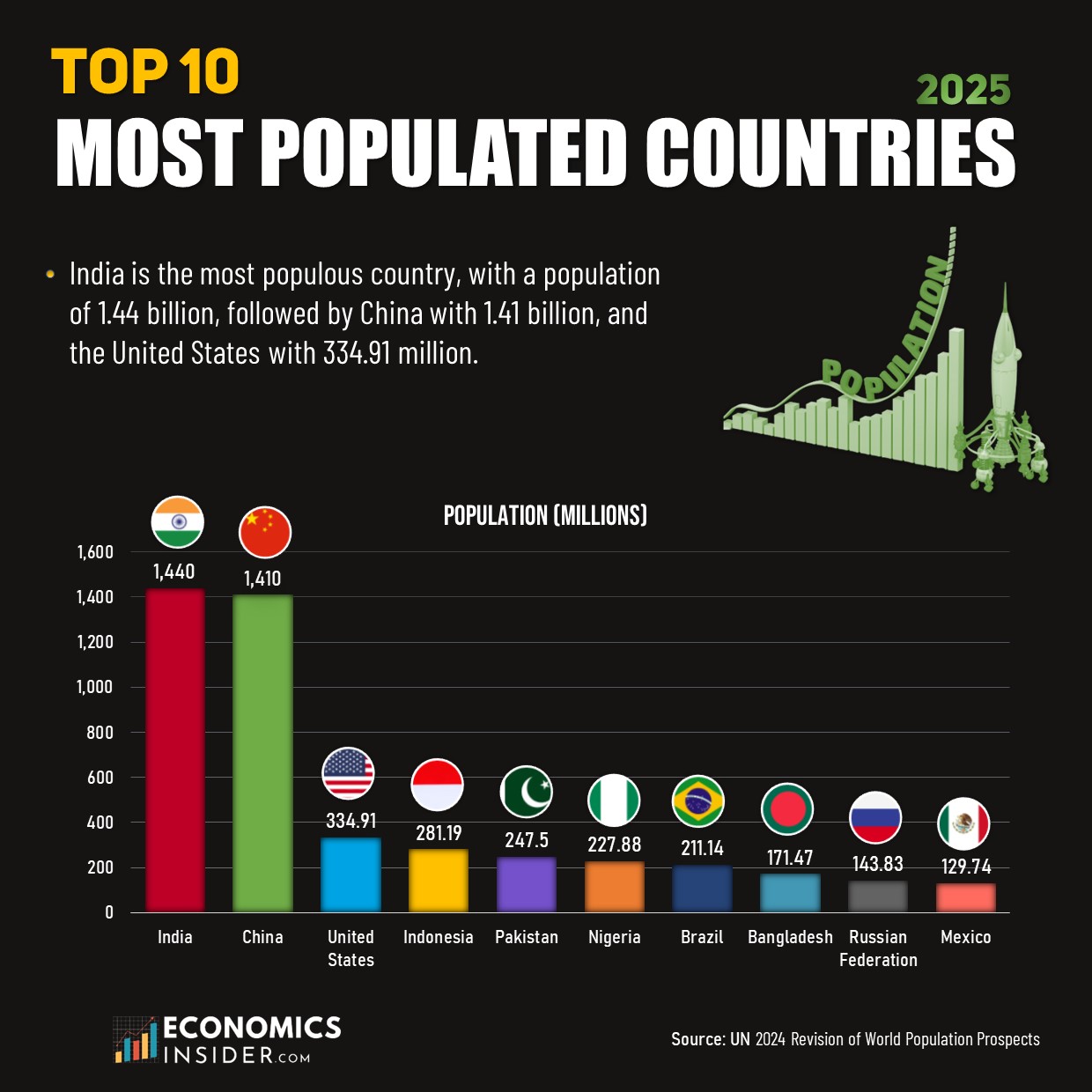
- The world population stands at around 8.2 billion people, and the 10 most populated countries together make up around 4.64 billion of them.
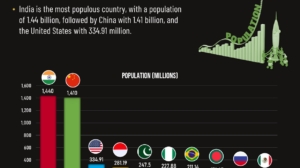
- India has the largest population at 1.44 billion, followed by China with 1.41 billion and the United States with 334.91 million.
- The population of some countries is growing rapidly, like Niger; however, countries like China and Russia are experiencing a declining population.
As per the United Nations Report, the world population has increased exponentially, from approximately 1 billion in 1800 to 8 billion at present. This is projected to grow further, reaching 9.8 billion by 2050 and 11.2 billion by 2100. Moreover, about 83 million individuals are added to the world population every year. This indicates that the world population is increasing at a record level, which is going to be a major challenge for scarce resources in the next few decades.
The 10 Most Populated Countries in the World
The table below presents the most populated countries in the world.
| Rank | Country | Most Recent Value | Continent/Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇮🇳 India | 1.44 billion | Asia |
| 2 | 🇨🇳 China | 1.41 billion | Asia |
| 3 | 🇺🇸 United States | 334.91 million | North America |
| 4 | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 281.19 million | Asia |
| 5 | 🇵🇰 Pakistan | 247.50 million | Asia |
| 6 | 🇳🇬 Nigeria | 227.88 million | Africa |
| 7 | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 211.14 million | South America |
| 8 | 🇧🇩 Bangladesh | 171.47 million | Asia |
| 9 | 🇷🇺 Russian Federation | 143.83 million | Europe/Asia |
| 10 | 🇲🇽 Mexico | 129.74 million | North America |
The data is collected from the following sources:
Population data is collected from “2024 Revision of World Population Prospects” and Statista.
Data related to population growth rate and total fertility rate have been sourced from the World Bank.
1. 🇮🇳 India – Population: 1.44 billion
India is the most populous nation in the world, which surpassed China in 2023. The population of the country is rising by 0.8% every year, with a fertility rate of 2.0 children per woman.
By 2030, India aims to become a high-middle-income country. However, challenges like housing shortages, pollution, and income inequality continue to impede its development. Additionally, India’s score of 0.633 in the Human Development Index (HDI) puts it in the medium human development category. It indicates the country’s notable progress in life expectancy and education in the country.
2. 🇨🇳 China – Population: 1.41 billion
China had been the world’s most populous country for decades before India overtook it in 2023. Its population is now slowly decreasing, with a growth rate of -0.1% and a fertility rate of 1.2 children per woman. China has enhanced the living standards for its huge population by increasing access to education, healthcare, and modern infrastructure.
According to the World Bank, China has raised more than 800 million people out of poverty since the beginning of its economic reforms in the late 1970s. China’s HDI value of 0.768 indicates considerable increases in life expectancy and education levels in the nation. Despite this progress, China still has challenges like an aging population and income disparities between regions, particularly between urban and rural regions.
Global Population Change by Generation in 2035
3. 🇺🇸 United States – Population: 334.91 million
The U.S. has a population of approximately 334 million, which makes it the third-most populous country in the world. Despite a much smaller population than India and China, the U.S. has one of the biggest economies in the world. Additionally, its population contributes about 4% towards the total global population and has been increasing by 0.5% per year. Both natural increases and net international migration together fuel the population growth in the US. By 2050, it is estimated that the US will have a population of 441 million.
Despite having the third largest population globally, U.S. population growth has slowed in recent years. The fertility rate in the United States has reduced to 1.7 children per woman. It indicates a long-term impact on population growth and demographic trends in the country. Moreover, the country is also facing numerous issues like income disparities, racial disparities, and the availability of low-cost healthcare for its huge population.
4. 🇮🇩 Indonesia – Population: 281.19 million
Indonesia is the fourth-most populous nation in the world, with a population of more than 281 million people. The population of the country is increasing at 0.7% annually, with a high fertility rate of 2.2 children per woman. Most of the Indonesian population lives on Java and Sumatra islands. Additionally, the country’s population is expected to keep increasing and reach an estimated 319 million by 2030.
5. 🇵🇰 Pakistan – Population: 247.50 million
Pakistan, with a population of more than 247 million, is the fifth-most populated nation in the world. Its population is increasing by approximately 2.0% every year, with a fertility rate of 3.6 children per woman. It indicates that Pakistan is among the world’s fastest-growing nations by population size. Pakistan’s population is expected to hit an estimated 263 million by 2030 and 344 million by 2050.
The high population growth rate poses a major challenge to the country’s economic, social, and environmental development. Yet, with a high youth bulge, Pakistan’s population offers prospects for a demographic dividend if managed well.
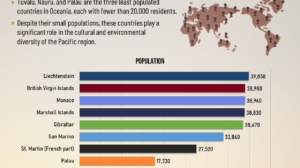
The countries with the lowest populations in the world
6. 🇳🇬 Nigeria – Population: 227.88 million
Nigeria is the most populated nation in Africa and the sixth most populated nation globally. With a population exceeding 227 million individuals, the country represents about 2.6% of the world’s population. Nigeria’s population is increasing at about 2.4% annually, which is among the world’s highest. In addition, this fast growth in Nigeria is supported by a high fertility rate of 5.1 children per woman, which is also among the highest globally.
Nigeria’s population is expected to continue increasing and reach approximately 443 million by 2050. Such a fast population growth rate poses major challenges for the economic, social, and environmental development of the country.
7. 🇧🇷 Brazil – Population: 211.14 million
With a population exceeding 211 million people, Brazil ranks as the largest country in South America and the seventh-largest country worldwide. The population of the country is increasing at 0.5% annually, which is driven by a fertility rate of 1.6 children per woman. Moreover, its population is also expected to grow to an estimated 233 million by 2030. The majority of Brazil’s population is concentrated in the southeast states of São Paulo, Rio de Janeiro, and Minas Gerais.
How Global Poverty Has Changed Over the Last 15 Years (2010-2024)
8. 🇧🇩 Bangladesh – Population: 171.47 million
Bangladesh, with a population of over 174 million, is the eighth most populous nation globally. The population of the country is increasing at a rate of 1.0% annually and is estimated to be around 200 million by 2050. Importantly, Bangladesh has been able to slow down its population growth rate, and its total fertility rate stands at 1.9 children per woman.
Despite its high population density, Bangladesh has made much progress in reducing poverty levels and improving the healthcare and education status of its people.
9. 🇷🇺 Russian Federation – Population: 143.83 million
With a population of around 143 million individuals, Russia is the world’s ninth-most populous nation. The country’s population has been declining since the 1990s, with a current growth rate of -0.3% per year. Russia’s population is estimated to decline further, falling to an estimated 135 million in 2050. Additionally, its population is aging, with a large percentage of Russians aged 65 years or older. This demographic trend in Russia poses significant challenges for the country’s economic growth, pension system, and labor market.
10. 🇲🇽 Mexico – Population: 129.74 million
Mexico has experienced significant population growth, largely due to its historically high birth rates. Throughout the 20th century, the country saw rapid growth due to high fertility rates. Moreover, large improvements in medical care have significantly lowered the infant mortality rate in the nation, leading to a larger population.
In addition to the most populated countries in the world, there are nations with populations counted only in the thousands. They are usually small island nations or territories and are characterized by different demographic features and cultures.
The 10 Least Populated Countries
The following table presents the 10 least populated countries in the world.
| Rank | Country | Most Recent Value | Continent/Region |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇹🇻 Tuvalu | 9,820 | Oceania |
| 2 | 🇳🇷 Nauru | 11,880 | Oceania |
| 3 | 🇵🇼 Palau | 17,730 | Oceania |
| 4 | 🇫🇷 St. Martin (French part) | 27,520 | Caribbean (Europe) |
| 5 | 🇸🇲 San Marino | 33,860 | Europe |
| 6 | 🇬🇮 Gibraltar | 38,470 | Europe |
| 7 | 🇲🇭 Marshall Islands | 38,830 | Oceania |
| 8 | 🇲🇨 Monaco | 38,960 | Europe |
| 9 | 🇬🇧 British Virgin Islands | 38,980 | Caribbean (North America) |
| 10 | 🇱🇮 Liechtenstein | 39,850 | Europe |
Conclusion
The total population of the top 10 most populated countries has reached about 4.64 billion people. This accounts for more than 50% of the global population, which is about 8.2 billion. No doubt, a large and growing population can benefit the country’s economy by providing a bigger workforce and a large consumer market. However, it also results in multiple issues like high demand for scarce resources, crowded cities, and pressure on public services.





















Add Comment