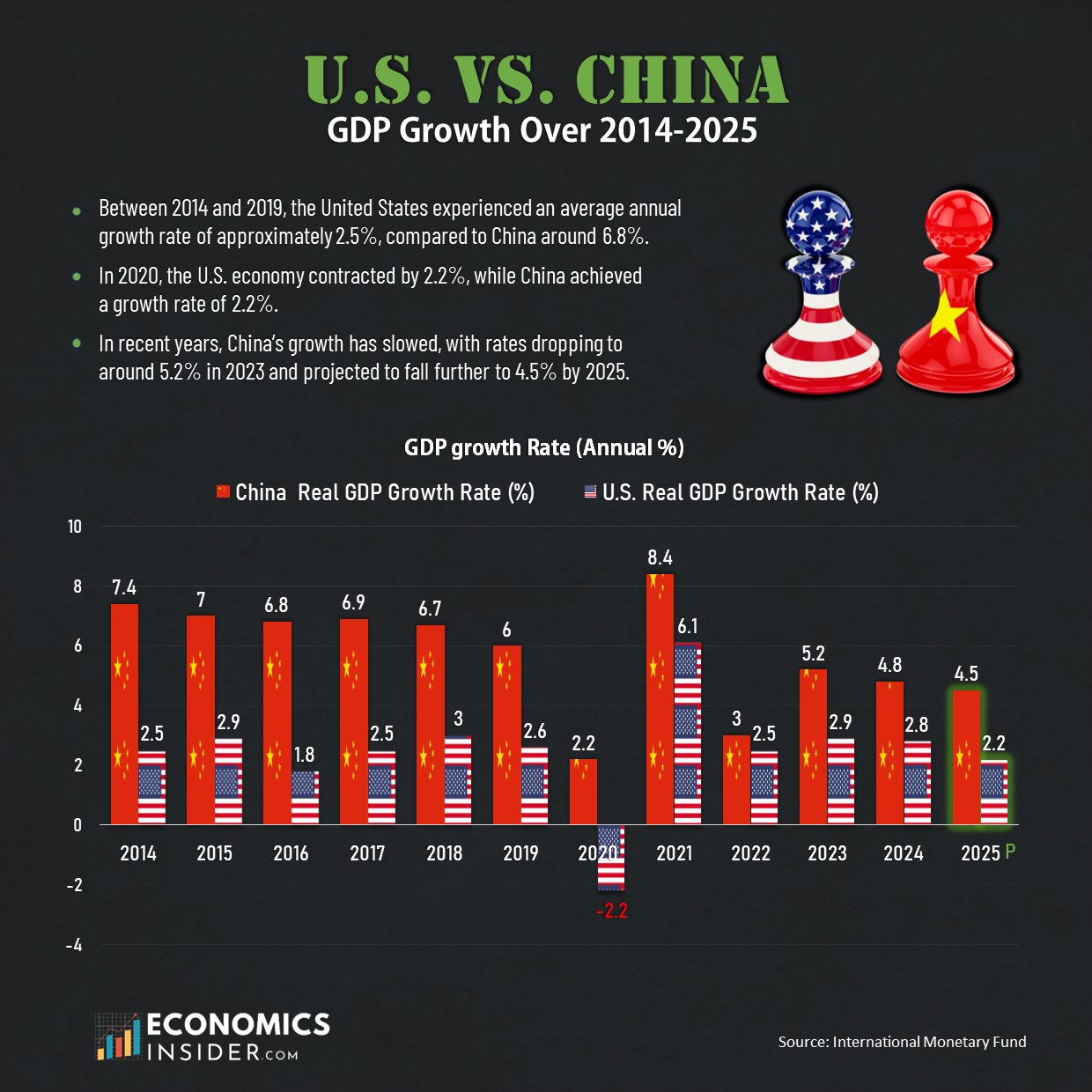
The United States and China are the world’s two biggest economies. China’s economy has expanded at a much faster rate compared to the U.S. over the last decade, though its growth has slowed in recent years. China’s real GDP growth rate average from 2014 to 2024 was about 5.85%, significantly higher than the U.S. average rate of 2.49%. Also, in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. economy shrunk by 2.2%, while China was able to grow by 2.2%. Nevertheless, the U.S. still remains the leading global economy because of its highest GDP and strong financial markets.
Key Takeaways
- From 2014 to 2024, China’s economy grew at an average rate of 5.85% per year, which was more than twice the U.S. average growth rate of 2.49%.
- The U.S. economy remains the world’s dominant economy despite growing much lower than China.
- Both countries are expected to see slower growth in 2025, with China’s growth rate projected to be higher than the U.S.
What is GDP growth rate?
GDP growth rate is an important economic indicator when looking at the economic performance of country. It quantifies the rise in the value of all goods and services manufactured in a nation over a period of one year. A high GDP growth rate signifies a booming economy, whereas a low or negative growth rate indicates economic challenges and downturns.
Comparing U.S. and China GDP Growth Rates
The table below presents the GDP growth rates of the U.S. and China from 2014 to 2024. Additionally, the table includes the projected GDP growth rates for both the U.S. and China in 2025.
| Year | 🇺🇸 U.S. (Real GDP growth rate) | 🇨🇳 China (Real GDP growth rate) |
|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 2.5% | 7.4% |
| 2015 | 2.9% | 7.0% |
| 2016 | 1.8% | 6.8% |
| 2017 | 2.5% | 6.9% |
| 2018 | 3.0% | 6.7% |
| 2019 | 2.6% | 6.0% |
| 2020 | -2.2% | 2.2% |
| 2021 | 6.1% | 8.4% |
| 2022 | 2.5% | 3.0% |
| 2023 | 2.9% | 5.2% |
| 2024 | 2.8% | 4.8% |
| 2025P | 2.2% | 4.5% |
The data is sourced from the International Monetary Fund.
This table indicates that over the past decade China’s growth rates have always remained above the United States. The following discussion will examine the growth rates of both economies from 2014-2025.
🇺🇸 US GDP Growth Rate
The US economy grows steadily, but at a slower pace compared to China. Here’s a breakdown of its growth trends:
Steady Growth (2014–2019): During these years, the US expanded at a rate of about 2.5% per annum on average. This expansion was fueled by strong consumer spending, a healthy services sector, and technological advancements.
The Pandemic Shock (2020): In 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic devastated the US economy, leading to a 2.2% contraction. Lockdowns, loss of jobs, and reduced consumer spending were the primary drivers of this negative growth rate.
The Strong Recovery (2021): With the huge government stimulus packages and rapid vaccine rollouts, the US economy recovered strongly in 2021, expanding at 6.1%. This was the highest U.S. growth rate for decades.
Return to Normal (2022–2025): After the pandemic period, the US growth rate has normalized at approximately 2.5% to 2.9%.
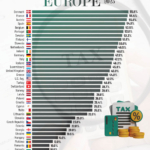
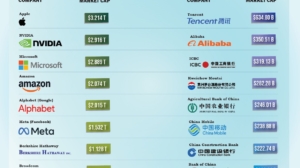
The 10 Largest U.S. Companies by Market Cap in 2025
🇨🇳 China’s GDP Growth
China’s economy, on the other hand, has been increasing at a significantly higher rate than that of the U.S. However, it’s slowing down in recent years.
Rapid Growth (2014–2019): The growth rates of China averaged approximately 6.8% annually in this decade. This was supported by the country’s enormous investment in infrastructure, manufacturing, and China’s global exports.
The Pandemic Impact (2020): Similar to the US, China too suffered from the pandemic, but its economy continued to grow by 2.2% in 2020. This was due to its strict lockdown policies and rapid recovery of the manufacturing sector.
The Post-Pandemic Boom (2021): China’s economy bounced back by 8.4% in 2021 due to robust exports and government-led investment initiatives.
Slowing Down (2022-2025): China’s growth has slowed in recent years, with rates falling to approximately 5.2% in 2023 and further expected to decline to 4.5% by 2025. This slowdown is due to factors such as an aging population, increasing debt, property market crises, and trade tensions with the US.
Why Is China Growing Faster Than the US?
China’s growth rates are always greater than the U.S. due to a variety of reasons. One of the main reasons is the level of economic development. The US is a mature economy, i.e., it is already a highly developed country. For such economies, 2–3% growth per annum is considered healthy. On the other hand, China is a developing nation. It has much scope for development, particularly in infrastructure, technology, and urbanization.
In addition, China has a huge population, which gives it a large and cheap labor force compared to the U.S. This has helped it to become the “world’s factory” and the largest exporter in the world market. Another key driver is China’s government-driven investments. The Chinese government is heavily involved in the economy by driving investments into strategic sectors such as infrastructure, technology, and manufacturing. Finally, China is the world’s largest exporter. Its capacity to manufacture at mass scale and export them worldwide has been one of the key contributors to its strong economic growth rates.
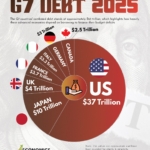
IMF Projects Stable Economic Growth for G7 Nations in 2025
The Future Outlook for Both Economies
Both the U.S. and China will experience slower growth in 2025 than their past high growth rates. For the U.S., the growth rate is forecasted to remain at 2.2% to 2.8%. This moderate growth is a sign of a more stable and mature economy but also suggests that the nation might struggle to sustain these growth rates amid increasing national debt, trade tensions, and inflation.
China’s growth is projected to slow to 4.5% to 4.8% by 2025, but it will remain above the U.S.
Conclusion
The U.S. and China have experienced different growth patterns over the past decade. The growth trend of these countries is driven by several factors including development stage, government policies, industrialization, and technology. China’s rapid growth in the earlier years was largely driven by industrialization and its massive exports globally. On the other hand, the U.S. economy has experienced steady growth, driven by advancements in innovation, technology, and the financial services sector.



















Add Comment