Emerging markets and developing economies play a major role in the world economy. While advanced economies, like the U.S., Japan, and parts of Europe, show slower growth, many developing countries still expand much faster. According to the World Economic Outlook, India is projected to grow faster than any other big emerging economy in 2026, with its GDP increasing by 6.2%. China also remains a big contributor to global growth, although slower than in the previous decade. China’s GDP is expected to grow by 4.2% in 2026.
Overall, emerging markets and developing economies are expected to grow by about 4.0% in 2026, down from 4.2% in 2025.
Key Takeaways
- Emerging markets are expected to expand by around 4.0% in 2026, well more than double the rate of advanced economies at around 1.6%.
- India leads the world in growth, with a projected GDP increase of 6.2% in 2026, while China’s growth is slowing to about 4.2%.
- Growth among emerging and developing economies is uneven, with some countries posting very strong increases and others faced with challenges ranging from high debt to inflation or weak investment.
Emerging Markets Growth Outlook
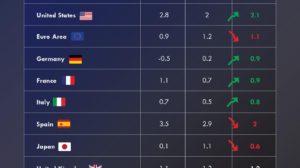
The following table shows the real GDP growth projections for emerging market and developing economies for 2026.
| Region / Country | 2024 | 2025 | 2026 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Emerging Market and Developing Economies (Total) | 4.3 | 4.2 | 4 |
| Emerging and Developing Asia | 5.3 | 5.2 | 4.7 |
| 🇨🇳 China | 5 | 4.8 | 4.2 |
| 🇮🇳 India | 6.5 | 6.6 | 6.2 |
| Emerging and Developing Europe | 3.5 | 1.8 | 2.2 |
| 🇷🇺 Russia | 4.3 | 0.6 | 1 |
| Latin America and the Caribbean | 2.4 | 2.4 | 2.3 |
| 🇧🇷 Brazil | 3.4 | 2.4 | 1.9 |
| 🇲🇽 Mexico | 1.4 | 1 | 1.5 |
| Middle East and Central Asia | 2.6 | 3.5 | 3.8 |
| 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | 2 | 4 | 4 |
| Sub-Saharan Africa | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.4 |
| 🇳🇬 Nigeria | 4.1 | 3.9 | 4.2 |
| 🇿🇦 South Africa | 0.5 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
Source: World Economic Outlook
India
India is the fourth-largest economy in the world in 2026, with an approximate GDP of $4.5 trillion. The country grew by about 6.5 percent in the year 2024, went up marginally to 6.6 percent in 2025, and is forecast to fall to 6.2 percent in 2026. Even with this small deceleration, India still remains the fastest-growing major economy in the world.
India’s growth is coming from heavy government spending on infrastructure, such as roads, railways, and energy projects. India also has seen rapid progress in digital payments, online services, and financial technology, while its IT and business services sector continues to grow.
China
China is the second-biggest economy in the world, after that of the U.S., with a GDP of about $20.6 trillion. It is growing more slowly. China’s economy grew by about 5.0% in 2024, slowed to 4.8% in 2025, and is expected to grow 4.2% in 2026. This slowdown is important when compared to the past. For many years, especially during the 2000s and early 2010s, China often grew at more than 10% per year. Now that the economy is much bigger and more mature, slower growth is normal.
China is facing several major problems. The property market crisis has reduced construction activity and lowered household confidence. Many local governments are under pressure because of high debt levels, which limit how much they can spend to support the economy. China is also dealing with an aging population and slower population growth, which affects its long-term economic potential.
Even so, China continues to invest heavily in manufacturing, artificial intelligence, electric vehicles, renewable energy, and technology.
Brasil
The Brazilian economy has been growing steadily in the past few years, but at a slowing pace. After registering 3.4% growth in 2024, the pace of growth is expected to slow down in 2025 and 2026. One of the main reasons for Brazil’s slowing growth is the central bank’s decision to keep interest rates high in order to control inflation. At times, the base policy rate has been raised, which makes loans more expensive for households and businesses. This slows spending and investment in the country.
Mexico and Russia
Mexico’s economy is expected to grow slowly, reaching about 1.0 % in 2025 and 1.5 % in 2026. Russia’s economic growth is also poor, around 0.6 % in 2025 and 1.0 % in 2026, mainly due to international sanctions, a shortage of workers, and difficulty in accessing international payments and investment.
Saudi Arabia
The economy of Saudi Arabia is doing well and is expected to grow by 4% in both 2025 and 2026. This is due to increased oil production and investment schemes in the Vision 2030 project initiated by the government.
Additionally, Nigeria’s economy is performing fairly well with a growth forecast of 3.9% for 2025 and 4.2% for 2026. But South Africa is expected to perform modestly with a meager growth level of 1.2% only for 2026.
Emerging and Developing Markets: Regional Performance
Emerging and developing Asia is the fastest-growing region, with growth of around 5.2% in 2025 and 4.7% in 2026. Latin America and the Caribbean are growing more slowly at about 2.4% in 2025 and 2.3% in 2026. The Middle East and Central Asia are improving, with growth rising from 3.5% to 3.8%. Emerging and developing Europe lags behind all regions at 1.8% in 2025 and 2.2% in 2026.
Conclusion
Emerging markets and developing economies continue to play a major role in the world’s economy. Their economies are growing much faster than those of advanced economies. The leading positions are taken by India, China, and other fast-developing regions of Asia, Africa, and the Middle East. Growth, however, is uneven. Some countries are benefiting from strong domestic demand, reforms, and investment; others face challenges like high debt, inflation, or structural problems that slow their progress.