Artificial intelligence (AI) is quickly penetrating almost all businesses, and it is changing how businesses work, make decisions, and serve customers. According to J.P. Morgan’s Guide to the Markets, about 17% of all businesses are using AI in at least one business function. Sectors like Information, Professional and Technical Services, and Finance and Insurance are leading AI adoption. These industries deal heavily with data, digital tools, and automation, which make AI easier to adopt and more valuable.
On the other hand, industries such as Transportation and Warehousing, Accommodation and Food Services, and Construction are far behind. These sectors rely more on physical labor and manual processes, which makes AI adoption slower and more difficult.
Key Takeaways
- AI adoption is highest in data-driven and knowledge-based industries, where digital tools are already deeply integrated into daily work.
- Service and physical-labor sectors are lagging behind in AI adoption.
AI Adoption Across Major Industries
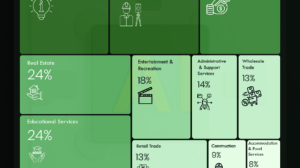
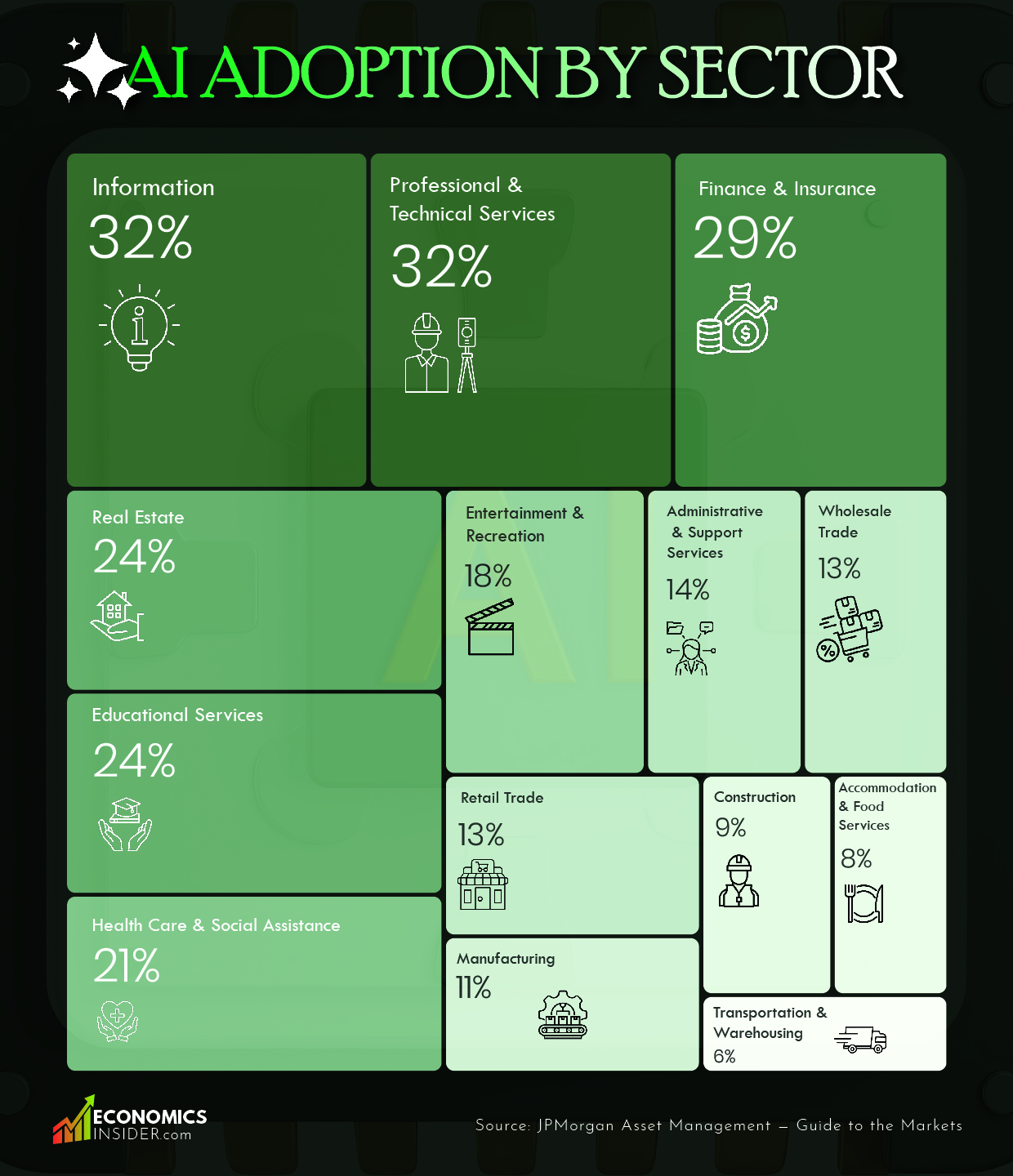
This table shows how many businesses in different industries are using AI in any business function as of December 2025.
| Sector | % of Firms Using AI (Dec 2025) |
|---|---|
| Information | 32% |
| Professional & Technical Services | 32% |
| Finance & Insurance | 29% |
| Real Estate | 24% |
| Educational Services | 24% |
| Health Care & Social Assistance | 21% |
| Entertainment & Recreation | 18% |
| Total (All Industries) | 17% |
| Administrative & Support Services | 14% |
| Wholesale Trade | 13% |
| Retail Trade | 13% |
| Manufacturing | 11% |
| Construction | 9% |
| Accommodation & Food Services | 8% |
| Transportation & Warehousing | 6% |
Source: JPMorgan Asset Management — Guide to the Markets
Information Sector (32%)
The Information sector has the highest AI adoption rate at 32%. This sector includes media, software, telecom, and Internet-based businesses. These sectors already handle large amounts of digital data, so it is no surprise that they can easily adopt AI.
The information sector utilizes AI for content recommendations, search, data analysis, and cybersecurity monitoring. Since the information sector relies heavily on technology, incorporating AI tools into this sector is relatively straightforward and inexpensive.
Professional and Technical Services (32%)
The adoption of AI technology in the Professional and Technical Services sector stands at 32%, which is equal to the Information sector. The sector includes consulting, engineering, legal, accounting, and research firms. The use of AI in this sector helps with document analysis, contracts, research, and forecasting. These companies benefit from AI technology because it helps to save time and costs.
Finance and Insurance (29%)
The Finance and Insurance sector, with 29% adoption, is another strong AI user. Banks, insurers, and investment firms rely heavily on data, risk assessment, and automation.
In finance and insurence common AI uses include:
- Fraud detection
- Credit scoring
- Customer service chatbots
- Risk and claims analysis
This sector has multiple incentives to adopt AI because small improvements in accuracy can save or earn millions of dollars.
Real Estate and Educational Services (24%)
Both real estate and educational services show a 24% AI adoption rate, which is above the overall business average. It means that these sectors are gradually embracing artificial intelligence even though they haven’t traditionally been tech-heavy.
In the real estate industry, AI is being used for things like predicting property prices, analyzing market trends, and creating virtual tours. AI tools can also handle routine tasks, such as chatbots answering questions, and automate property valuations faster and more accurately. Many real estate firms see AI as a future, and the technology is projected to grow even more quickly in the next few years as more companies invest in it.
In education, AI is making the process of learning more individualized. It enables personalized learning tools, automated grading systems, and methods of tracking and enhancing student performance. Educational platforms can adapt the lessons to the pace of every particular student, provide immediate feedback on the completion of various assignments, and relieve teachers from tedious tasks so that they can be more focused on teaching.
Sectors with Lower AI Adoption
Industries like Retail Trade (13%), Manufacturing (11%), and Construction (9%) are behind the overall average of adopting AI in businesses. This is because they generally operate on thin margins and require both physical infrastructure and manpower. While in these industries, AI technology can also assist with inventory management, forecasting, and quality control.
The lowest levels of adoption for AI are Transporting & Warehousing, at 6%, and Accommodation & Food Services, at 8%.
Conclusion
The adoption of AI is not balanced between sectors. The sectors that involve knowledge and digitization are adopting AI at a fast rate, whereas sectors that involve physical and service-related activities are adopting AI at a slow pace. Sectors that adopt AI at an earlier stage gain more advantages in terms of productivity, efficiency, and competitiveness.