Government debt as a percentage of GDP indicates the level of debt a country owes relative to its size of economy. If a nation has a high debt to GDP ratio, then it owes a more money than the value of what it produces in a year.
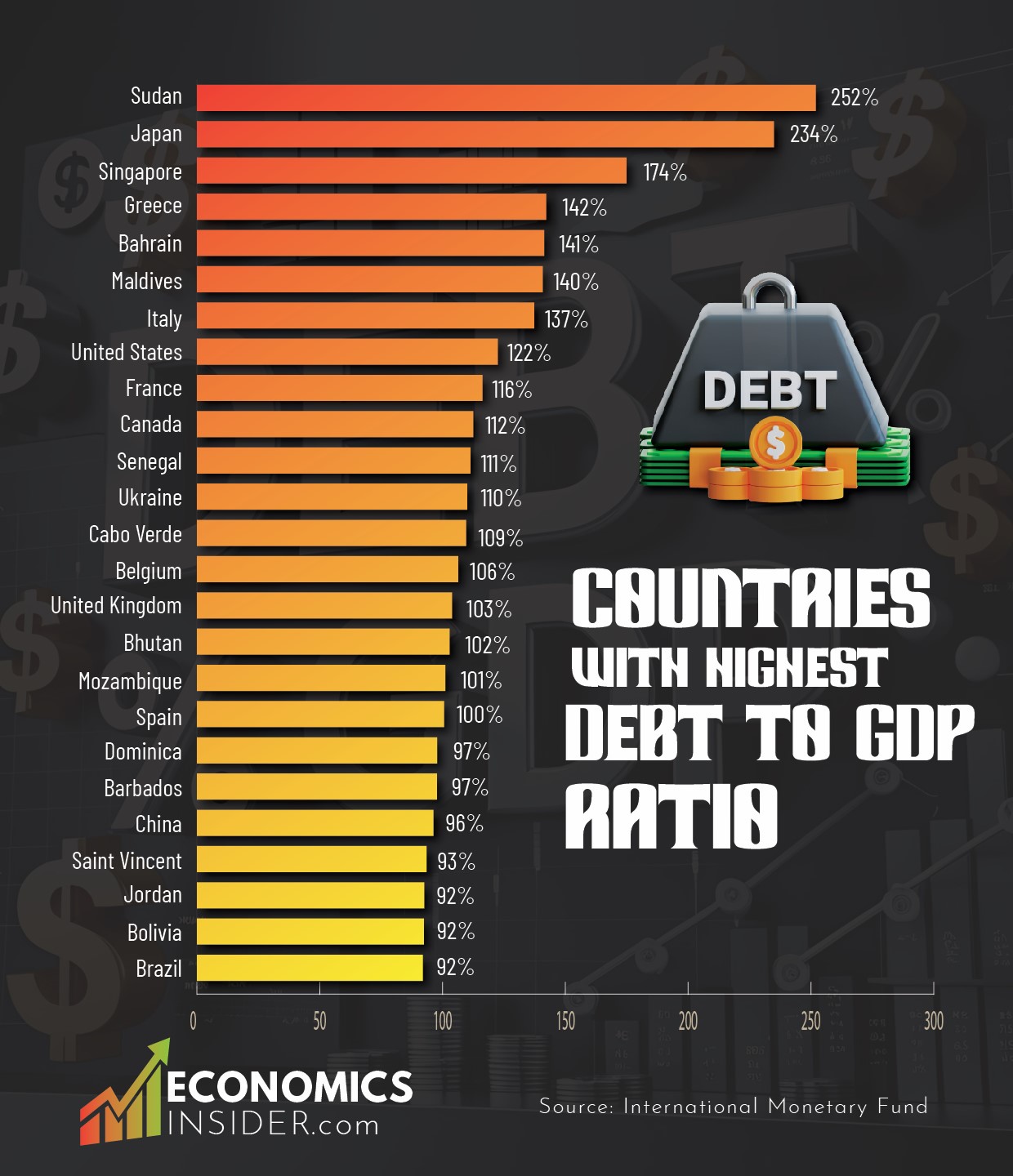
According to the International Monetary Fund, Sudan has the highest debt-to-GDP ratio in the world. However, because of its relatively small economy, the country’s total debt is not as large as that of the United States. Japan, the world fifth fifth-largest economy, has the second-highest debt-to-GDP ratio despite being one of the biggest economies in the world. The US, Italy, and Greece also have debt more than their total economic output.
Key Takeaways
- Sudan, a country located in Africa, has the highest debt-to-GDP ratio in the world at 252%.
- The world’s two largest economies, the United States and China, have high debt-to-GDP ratios. The U.S. stands at 122%, which is high, while that of China stands at 96%.
Top 25 Countries with High Debt To GDP Ratio
The following table shows the top 25 countries with the largest general government debt to GDP ratio. It indicates the countries with the biggest debts as a proportion of the economy’s size.
| Rank | Country | Debt (% of GDP) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇸🇩 Sudan | 252% |
| 2 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 235% |
| 3 | 🇸🇬 Singapore | 175% |
| 4 | 🇬🇷 Greece | 142% |
| 5 | 🇧🇭 Bahrain | 141% |
| 6 | 🇲🇻 Maldives | 141% |
| 7 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 137% |
| 8 | 🇺🇸 United States | 123% |
| 9 | 🇫🇷 France | 116% |
| 10 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 113% |
| 11 | 🇸🇳 Senegal | 111% |
| 12 | 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 110% |
| 13 | 🇨🇻 Cabo Verde | 110% |
| 14 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | 106% |
| 15 | 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 104% |
| 16 | 🇧🇹 Bhutan | 103% |
| 17 | 🇲🇿 Mozambique | 101% |
| 18 | 🇪🇸 Spain | 101% |
| 19 | 🇩🇲 Dominica | 98% |
| 20 | 🇧🇧 Barbados | 98% |
| 21 | 🇨🇳 China | 96% |
| 22 | 🇻🇨 Saint Vincent | 94% |
| 23 | 🇯🇴 Jordan | 93% |
| 24 | 🇧🇴 Bolivia | 92% |
| 25 | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 92% |
The data is sourced from the International Monetary Fund.
🇸🇩 Sudan
Sudan has the highest debt to GDP ratio in the world at 252%. War, political instability, and the loss of oil revenues after the secession of South Sudan have all been contributing factors in the country’s enormous debt burden.
Sudan is also one of the poorest countries in the world, which is grappling with high inflation, depreciation of currency, and increased economic suffering for millions of people. The rising debt in the country makes it challenging for the government to spend on essential infrastructure such as schools, hospitals, and roads.
🇯🇵 Japan
Japan is the fifth largest economy in the world, which has the second largest debt as a percentage of GDP globally at 234%. The country began to borrow extensively in the 1990s to combat economic slowdown following a massive financial bubble. Additionally, the country is facing one of the severe demographic challenges with an ageing population.
The good thing about Japan’s debt is that a major share of Japan’s debt is held domestically by its citizens and institutions, which reduces its default risk despite a high debt-to-GDP ratio.
🇺🇸 United States
The United States is the world’s largest economy by nominal GDP and the second largest by GDP measured at purchasing power parity (PPP). The country has one of the highest debt-to-GDP ratios in the world among advanced economies at 122%. The US debt has reached about $36 trillion in 2025 and is increasing by almost $1 trillion every 100 days.
Although the US has much lower debt to gdp ratio compared to Sudan and japan, but its absolute debt is much higher then these countries. In absolute terms US has the largest debt globally. The country has borrowed much in the past to fund wars, social programs, and economic assistance during crises like financial crises and COVID-19.
However, the U.S. dollar is the world’s largest reserve currency, which makes it cheaper for the U.S. to borrow and handle its debt. Additionally, the rapidly rising US debt also rising interest payments and fewer funds available for other manadatory spending.
🇨🇳 China
China’s debt as a percentage of GDP stands at 96%, which is much lower than the United States. China’s debt has grown extremely fast due to massive spending on infrastructure and local government initiatives to fuel economic growth. A continuously rising debt to GDP may potentially make it harder for China to keep growing strongly in the future.
🇸🇬 Singapore
Singapore’s debt-to-GDP ratio is 174%, the third highest on the list. But Singapore’s debt situation is unique. The country doesn’t borrow to narrow down the budget deficit but to develop a strong debt market and invest through its wealth funds.
🇬🇷 Greece
Greece experienced a huge debt crisis beginning in 2009, which was followed by bailouts and tight austerity measures. Although the nation is making strides in economic growth, its economy continues to struggle with the huge debt burden. High debt constrains government expenditure on development and increases the cost of borrowing in Greece.
🇮🇹 Italy
Italy has suffered from political and slow economic growth for decades. Therefore, the country’s debt as a percentage of GDP has reached almost 140%.
Besides the top-ranked countries already noted, there are several other high-ranking countries with high debt to GDP ratios globally. France’s debt-to-GDP ratio stands at 116.3%. The country borrowed heavily to finance social programs and economic development. Canada comes in at 112%, its percentage grew higher in more recent years based on pandemic-related spending and relief efforts.
The United Kingdom comes in at 103%, reflecting years of borrowing to offset economic slumps like the 2008 financial crisis as well as the UK’s withdrawal from the EU, or Brexit. Spain also comes in on the list at 100%, as it had high borrowing requirements during the Eurozone crisis, as well as to sustain its economy through the COVID-19 pandemic. Overall, these countries reflect that a high debt-to-GDP ratio is not a problem for poor or unstable countries — it can happen anywhere in the advanced and developed countries.
Conclusion
Looking at the data shows that more than 15 countries have surpassed the 100% debt-to-GDP ratio. This is a big issue that exists in developed and emerging markets. Sudan has the highest ratio in the world due to decades of war and economic decline. Japan has had high debt for decades, and yet it still limits future options. The United States and China show that even large and powerful economies have the problem of growing debt levels.



















Add Comment