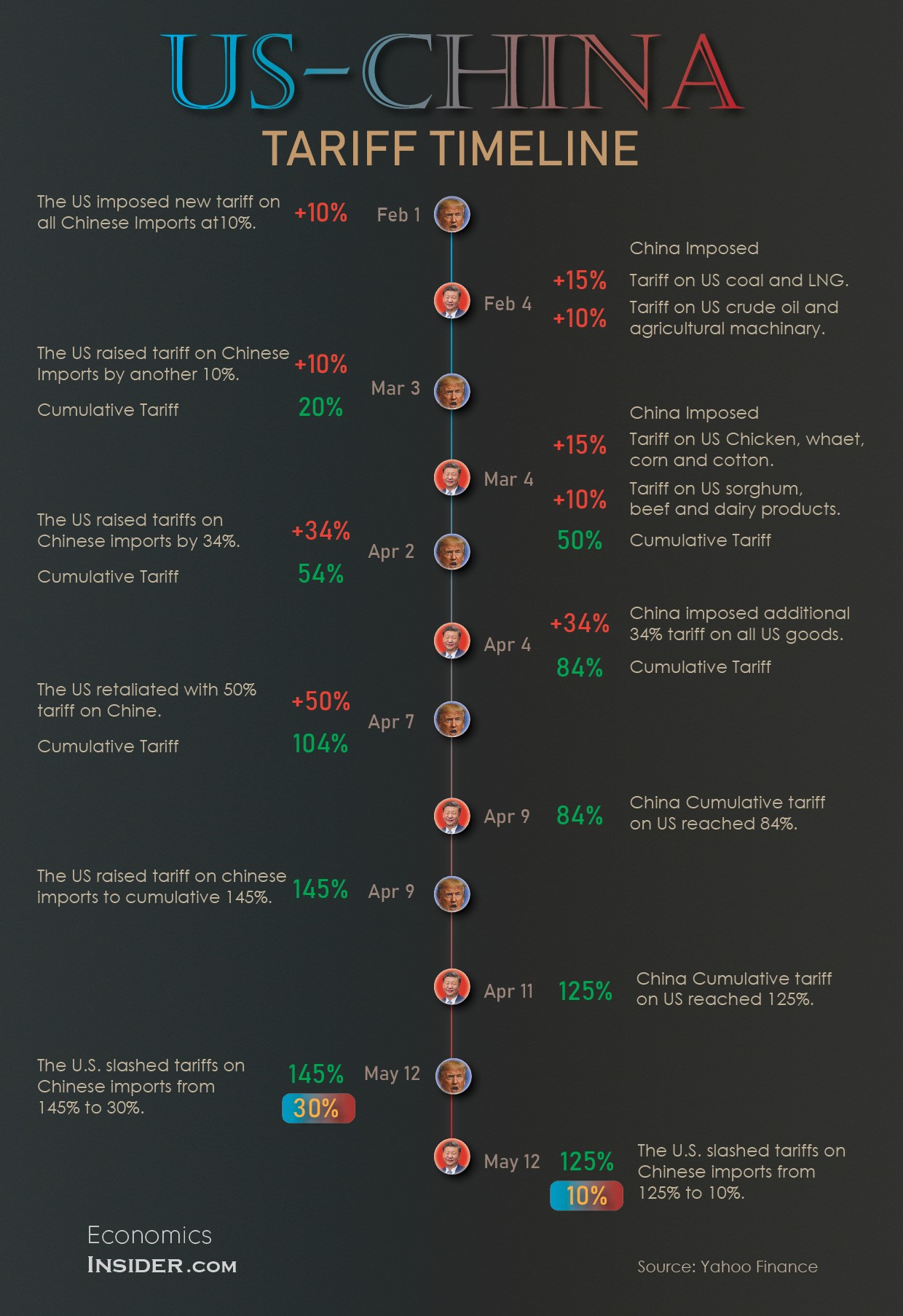
The US China tariff war flared up once again following the start of President Trump’s second term. Beginning in early February, both nations started imposing hefty tariffs on the other’s products. The U.S. tariff on Chinese products hit a whopping 145%, and China retaliated with tariffs up to 125% on American goods. These tit-for-tat measures raised fears of recession across the global economy.
However, on May 12, both countries committed to suspending most of the tariffs for 90 days in a bid to de-escalate trade tensions. The development followed talks in Switzerland, where both governments agreed to reduce tariffs on each other. As part of the truce, the United States slashed its tariffs from 145% to 30%, while China reduced its tariffs from 125% to 10%. While it doesn’t end the US-China tariff war, it marks a big step toward easing tensions between the world’s two largest economies.
Key Takeaways
- In just over two months, U.S. tariffs on Chinese goods surged from 10% to 145%, while China’s retaliatory tariffs on U.S. imports jumped to 125%.
- On May 12, 2025, both countries agreed to reduce tariffs. The U.S. lowered its tariffs on Chinese goods from 145% to 30%, while China cut its tariffs on American imports from 125% to 10%.
- hh
US-China Tariff Timeline
A look at how US-China tariffs escalated, month by month, until the May pause agreement.
| Date | 🇺🇸 United States Action | 🇨🇳 China’s Response |
|---|---|---|
| Feb-01 | Imposed 10% tariff on all Chinese imports | |
| Feb-04 | 15% on U.S. coal, gas; 10% on crude oil, vehicles | |
| Mar-03 | Increased tariff by 10% (total 20%) | |
| Mar-04 | 15% on chicken, wheat, corn; 10% on soybeans and other farm exports. | |
| Apr-02 | Added 34% tariff (total 54%) | |
| Apr-04 | 34% on all U.S. goods | |
| Apr-07 | Added 50% (total 104%) | |
| Apr-09 | Increased to 145%, no relief for China | China raised tariffs to 84% |
| Apr-11 | Removed tariffs on others, kept 20% on China | China raised tariffs to 125% |
| May-12 | Dropped tariffs to 30% (pause deal) | Dropped tariffs to 10% (pause deal) |
The data is sourced from Yahoo Finance.
A Timeline of US China Tariff Escalation and Pause
It is based on the data from Yahoo Finance.
- February 1: The U.S. imposed a new 10% tariff on all Chinese imports, reigniting the US-China tariff war between the world’s two largest economies.
- February 4: China responded with a range of new tariffs on American energy and industrial goods. China slapped a 15% tariff on U.S. coal and natural gas and a 10% tariff on U.S. crude oil, farm equipment, and large vehicles.
- March 3: The U.S. increased its tariff rate on Chinese goods by an additional 10%, bringing the total to 20%.
- March 4: China imposed 15% tariffs on chicken, wheat, corn, and cotton, and 10% tariffs on soybeans, pork, and other key farm exports.
- April 2–7: Things spiraled quickly. On April 2, the U.S. imposed an additional 34% tariff on Chinese goods, raising the total U.S. tariff on Chinese imports to 54%. China responded on April 4 with a 34% tariff on all U.S. goods. Just three days later, on April 7, the U.S. escalated further, adding another 50%, bringing the total U.S. tariff rate to 104%.
- April 9: The U.S. granted a temporary 90-day tariff relief to most of its trading partners. China was notably excluded from this concession. Additionally, the U.S. increased its tariffs on Chinese goods to a staggering 145%.
- April 11: China raised its tariffs to 125% on U.S. goods, intensifying the US-China tariff conflict.
- May 12: Both countries agreed to a 90-day pause in the trade war, marking a major de-escalation in the ongoing U.S.-China tariff dispute.
A 90-Day Pause in Most Tariffs
The U.S. and China agreed to a temporary truce starting May 14. This deal came after important discussions in Switzerland. Under the agreement, the U.S. reduced its tariffs on Chinese imports from 145% to 30%, and China lowered its tariffs on U.S. goods from 125% to 10%.
However, this isn’t a full resolution. The agreement lasts 90 days. President Trump said that if talks don’t move forward during this period, the suspended U.S. tariffs on Chinese goods could come back.
How the US-China Tariff War Began
The U.S.-China tariff war has been brewing for decades. It began as a disagreement over trade imbalances, intellectual property theft, and technology. In 2018, under the presidency of Donald Trump, the U.S. started imposing tariffs on billions of dollars’ worth of Chinese products to push China to more equitable trade terms. China retaliated with its own tariffs.
The trade war was marked by rounds of negotiations, broken agreements, and constant escalations. It flared up again in early 2025 with the beginning of Trump’s second term as U.S. president.
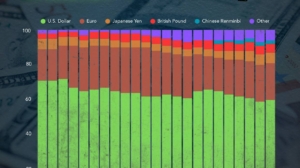
US Dollar Dominance in International Finance
US-China Trade Deficit
At the heart of the U.S.-China tariff conflict is the huge U.S. trade deficit with China. In 2024, this gap reached about $295 billion. The U.S. exported $144 billion worth of goods to China but imported roughly $439 billion in return.
China remains the biggest contributor to the U.S. trade deficit. Other countries like Mexico and Vietnam also rank high, but the China deficit is by far the largest. Overall, the U.S. trade deficit with its top ten trading partners nears $1 trillion.
Conclusion
The past few months showed how quickly trade tensions can spiral. Tariffs hit new highs during the peak of the US-China tariff war. The United States imposed up to 145% tariffs on Chinese goods. As a reaction, China upped its tariffs to 125% on most U.S. products. But both countries have now suspended most tariffs for 90 days. Although it does not end the trade war, it brings hope for future negotiations and long-term peace. However, the U.S.-China trade relationship is still on shaky grounds.




















Add Comment