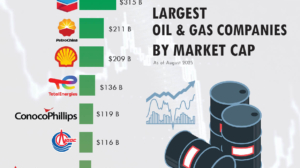
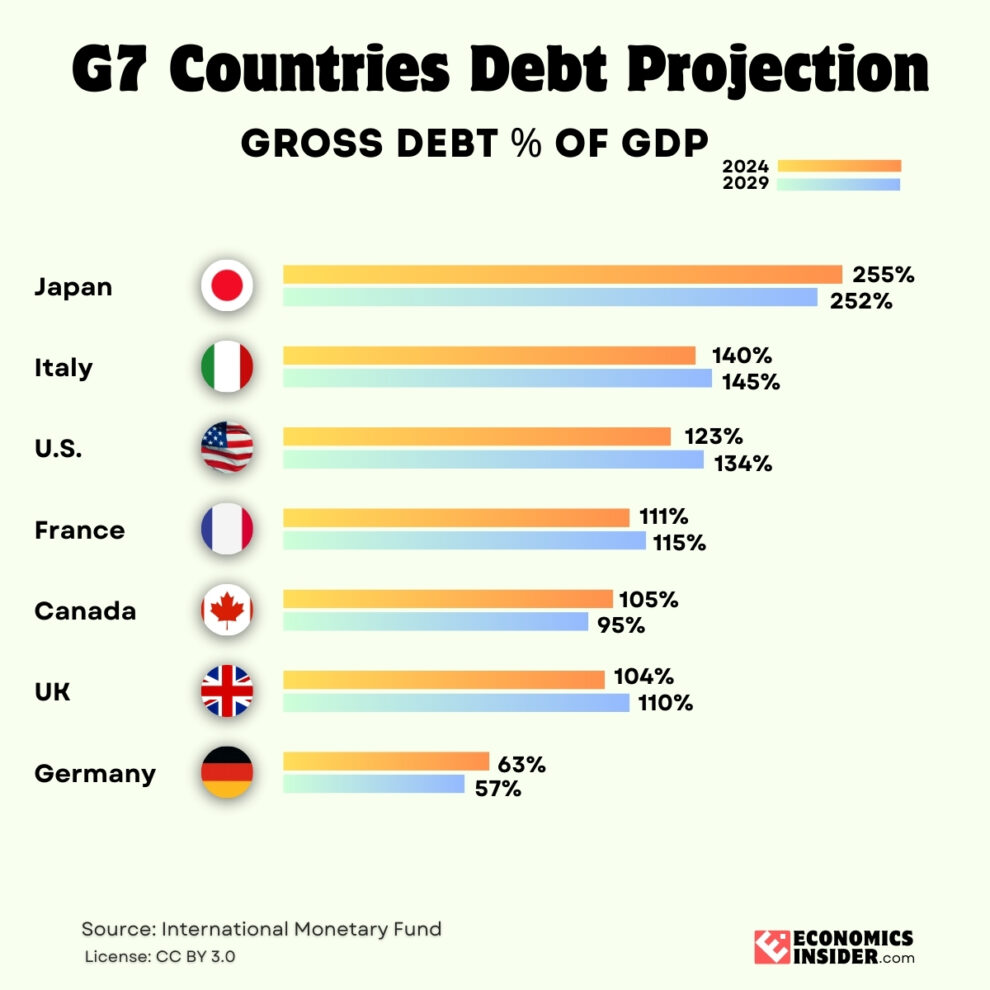
The global debt has ballooned to a staggering $315 trillion in 2024. The debt-to-GDP ratio among G7 countries is expected to follow a mixed trend in the next five years. While some nations are likely to stabilize their debt levels, others may experience a continued increase in their debt burden.
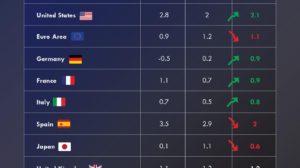
The G7 countries are some of the world’s largest economies, including the US, Canada, Germany, France, the UK, Italy, and Japan. Among G7 countries, the United States has the highest absolute debt of approximately $36 trillion with a debt-to-GDP ratio of 123%. Also, Japan has the highest debt-to-GDP ratio of approximately 250%, but it has lower debt as compared to the US.
What is Gross Debt?
According to the IMF, gross debt consists of total liabilities that require payment by the debtor to the creditor at a given time. This includes various forms of debt liabilities, such as SDRs, currency and deposits, debt securities, loans, insurance, pensions and standardized guarantee schemes, and other accounts payable.
The table below presents the G7 nations debt projections for the next five years (2024-2029).
| Country | Government gross debt (% of GDP) 2024 | Government gross debt (% of GDP) 2029 |
|---|---|---|
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 254.6% | 251.7% |
| 🇮🇹 Italy | 139.2% | 144.9% |
| 🇺🇸 U.S. | 123.3% | 133.9% |
| 🇫🇷 France | 111.6% | 115.2% |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | 104.7% | 95.4% |
| 🇬🇧 UK | 104.3% | 110.1% |
| 🇩🇪 Germany | 63.7% | 57.7% |
Source: International Monetary Fund
G7 Countries Debt Profile
Germany, Canada, and Japan are on track to lower their debt-to-GDP ratios in the coming five years. It means they’ll be managing their debt better compared to the size of their economies. On the other hand, the U.S., the U.K., France, and Italy are expected to see their debt-to-GDP ratio increase. For these countries, rising debt could become a bigger challenge amid slower economic growth and higher government spending.
The U.S. national debt, which is about 123% of the country’s total economic output (GDP), is expected to rise 133% by 2029. The country’s total debt is set to keep growing, reaching $35 trillion in 2024. The rapid rise in US debt is due to increased government spending, low government revenue, economic slowdowns, and rising interest rates.
Japan has the highest debt-to-GDP ratio of about 255% compared to the size of its economy. However, Japan’s debt is expected to reduce by about 3% by 2029. While this might seem like a small decrease, it’s a step toward better financial stability for a country that’s been dealing with a high debt-to-GDP ratio for many years.
Canada is projected to experience the largest decline in its debt-to-GDP ratio over the next five years. The country’s debt-to-GDP ratio is projected to decline from 105% to approximately 95% by 2029.
Conclusion
The debt can help fund important projects and services, but too much debt can create financial risks in the long run. Among the G7 nations, the US has the highest absolute debt, which has reached over $36 trillion in 2025. Additionally, Japan has the highest debt-to-GDP ratio among G7 countries, which has surpassed 250% of its GDP. In contrast, Germany has the lowest debt-to-GDP ratio of approximately 63% among G7 countries.




















Add Comment