Exports play a key role in the country’s economic development and growth. Some countries heavily sell goods and services abroad, while others rely more on domestic consumption to drive their economies.
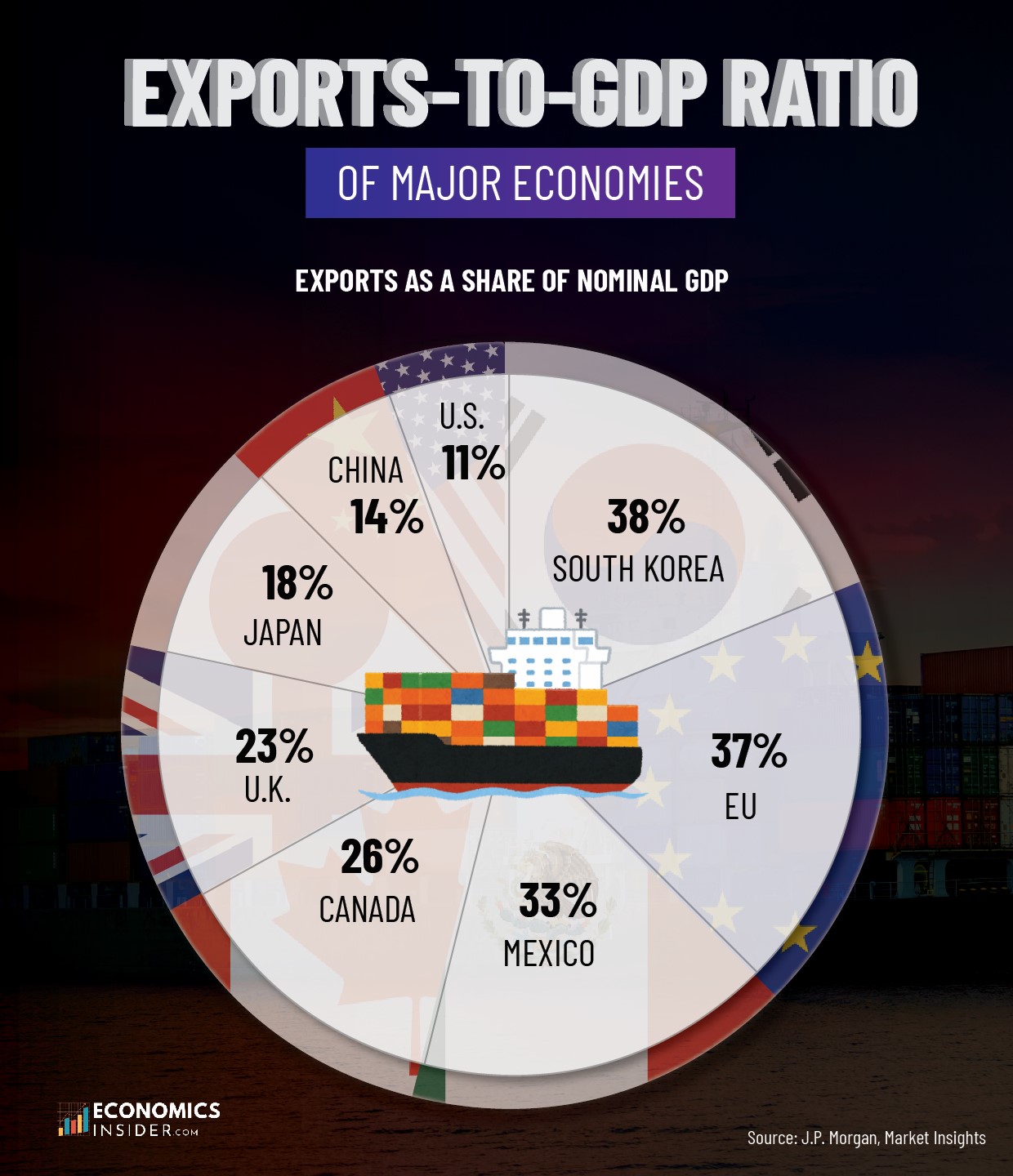
According to a report by J.P. Morgan Asset Management, countries like South Korea and Mexico have the highest export-to-GDP ratio compared to major economies such as the United States and China. The EU as a collective bloc is also more export-dependent with approximately 37% export-to-GDP ratio. Additionally, many advanced economies still maintain strong export links, but their levels vary significantly based on geography, trade relationships, and economic structure.
Key Takeaways
- Smaller economies like South Korea and Mexico rely more on exports than larger economies like the U.S. or China.
- The EU as a collective bloc is more export-dependent and close to the level of South Korea.
- Advanced economies with large domestic markets tend to have lower export-to-GDP ratios.
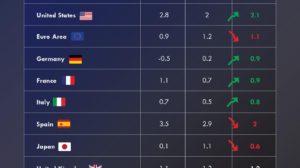
Exports-to-GDP Ratio of Key Economies
The following table shows the share of exports as a percentage of nominal GDP in 2023 for a selection of key economies.
| Country | Exports-to-GDP Ratio |
|---|---|
| 🇰🇷 South Korea | 38% |
| 🇪🇺 EU | 37% |
| 🇲🇽 Mexico | 33% |
| 🇨🇦 Canada | 26% |
| 🇬🇧 U.K. | 23% |
| 🇯🇵 Japan | 18% |
| 🇨🇳 China | 14% |
| 🇺🇸 U.S. | 11% |
The data is sourced from a report by J.P. Morgan Asset Management.
Across the eight major economies, export dependency ranges from as high as 38% to as low as 11%. South Korea tops the list, while the United States is at the bottom. The European Union, Mexico, and Canada also show strong export dependency relative to their economic size. On the other hand, Japan, China, and the U.K. fall somewhere in the middle.
🇰🇷 South Korea
South Korea stands out with exports making up 38% of its GDP. This reflects its deep integration into global supply chains, especially in electronics, semiconductors, automobiles, and shipbuilding. According to the Observatory of Economic Complexity, South Korea’s top exports in 2025 include integrated circuits, automobiles, refined petroleum, passenger and cargo ships, and office machine parts. Additionally, the country’s year-on-year growth of exports is primarily driven by its increased exports to the United States ($1.24B, 12.5%), Chinese Taipei ($1.07B, 39%), and Hong Kong ($812M, 42.9%).
Its high exports-to-GDP ratio shows the country’s reliance on trade, which has also fueled South Korea’s rapid industrial growth and prosperity over the past few decades.
🇪🇺 The European Union
The European Union comes in just behind South Korea, with an export-to-GDP ratio accounts for 37%. As a bloc, the EU leverages benefits from internal trade among member countries and from strong export markets worldwide. According to the Eurostat, the euro area recorded a trade surplus of €36.8 billion, with exports of goods to the rest of the world totaling €279.8 billion and imports amounting to €243.0 billion.
Germany, in particular, contributes much of the EU exports with its manufacturing and automotive sectors. The EU’s single market, common trade policy, and advanced infrastructure make it one of the most export-oriented economies globally.
🇲🇽 Mexico
Mexico’s exports make up 33% of its GDP. The country’s large portion of exports comes from manufactured goods, especially vehicles, electronics, and machinery. Additionally, Mexico’s close trade ties with the United States and its trade agreements like USMCA have boosted its role as a key manufacturing hub.
🇨🇦 Canada
Canada has a 26% export-to-GDP ratio. The majority of its exports are driven by natural resources, energy, and manufacturing. Additionally, Canada is one of the largest trading partners of the United States, which accounts for about 75% of its export market.
🇯🇵 Japan
Japan’s export-to-GDP ratio stands at 18%. Japan is the fifth-largest economy in the world, with a GDP of approximately $4 trillion. Japan exports Cars, Machines and apparatus, semiconductor devices, electronic integrated circuits, and Motor vehicles globally. Although Japan has a large economy and export base, its aging population and mature economy are lowering its growth rate.
🇨🇳 China
China is often referred to global export powerhouse due to its much larger export base all over the world. The country’s export-to-GDP ratio stands at 14%, which is much lower than in many other countries. However, China is the second-largest economy in the world after the United States, with a GDP of approximately $19 trillion. Even a 14% exports-to-GDP ratio accounts for over $2.5 trillion. While China exports a vast array of goods worldwide, its large domestic market reduces the relative share of exports in its overall economy.
🇺🇸 United States
At the bottom of the list is the U.S., with exports accounting for just 11% of GDP. Although the country has a lower export-to-GDP ratio and relies less on foreign markets, its exports still account for approximately $3 trillion due to its massive GDP of approximately $30 trillion. The top exports of the United States are Aircraft parts, petroleum products, and financial services.
Conclusion
Countries like South Korea and Mexico, though much smaller in economic size compared to the United States and China, depend heavily on exports to drive their economies. In contrast, economic giants such as the U.S. and China rely more on domestic demand. As a collective bloc, the European Union is more export-oriented and falls closer to South Korea in terms of export dependence. Generally, advanced economies with large domestic markets tend to have lower export-to-GDP ratios.


















Add Comment