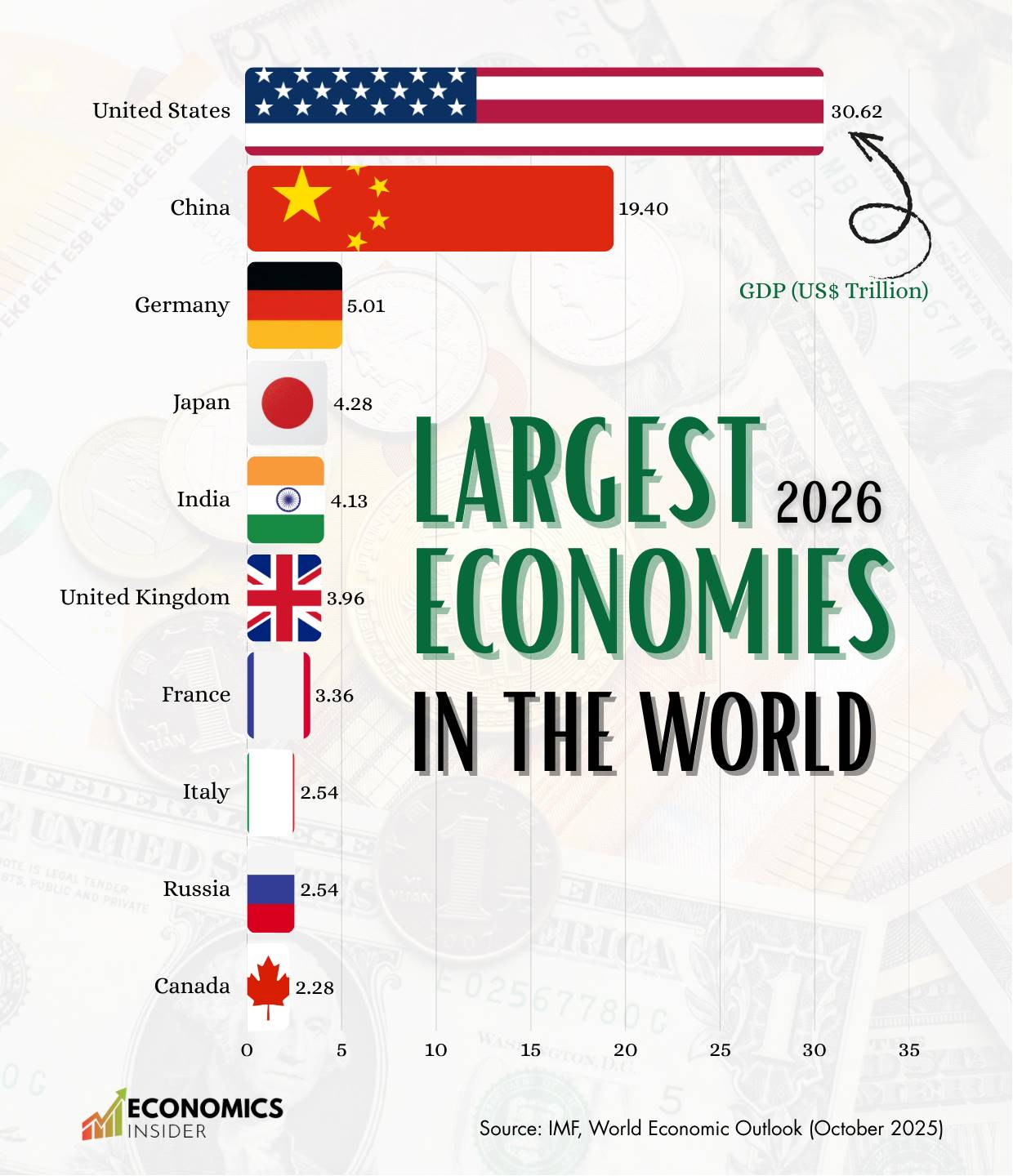
The total value of all goods and services produced (GDP) around the world in 2026 is estimated to be about $117.17 trillion. The United States and China remained the world’s two largest economies. Together, these two countries account for nearly $50 trillion of the world’s economic output or GDP.
They are followed by other major economies such as Germany, Japan, India, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, Canada, and Russia. These countries consistently rank among the largest economies in the world by nominal GDP. Additionally, these nations play a major role in international trade, finance, and innovation.
What is GDP?
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a key economic indicator used to assess a country’s economic growth. It represents the total monetary value of all final goods and services produced within a country’s borders. A higher GDP generally signifies a healthy and growing economy, while a lower GDP indicates economic challenges or weaknesses.
Key Takeaways
- The United States and China dominate the global economy, together contributing nearly half of the world’s total GDP of $117.17 trillion in 2026.
- Other top economies, including Germany, Japan, India, the United Kingdom, France, Italy, Russia, and Canada, also play a major role in global trade and economy.
Largest economies in the world
The following table provides a ranking of the world’s largest economies based on nominal GDP.
| Rank | Country | GDP (Billion USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 🇺🇸 United States | 30,620 |
| 2 | 🇨🇳 China, People’s Republic of | 19,400 |
| 3 | 🇩🇪 Germany | 5,010 |
| 4 | 🇯🇵 Japan | 4,280 |
| 5 | 🇮🇳 India | 4,130 |
| 6 | 🇬🇧 United Kingdom | 3,960 |
| 7 | 🇫🇷 France | 3,360 |
| 8 | 🇮🇹 Italy | 2,540 |
| 9 | 🇷🇺 Russian Federation | 2,540 |
| 10 | 🇨🇦 Canada | 2,280 |
| 11 | 🇧🇷 Brazil | 2,260 |
| 12 | 🇪🇸 Spain | 1,890 |
| 13 | 🇲🇽 Mexico | 1,860 |
| 14 | 🇰🇷 Korea, Republic of | 1,860 |
| 15 | 🇦🇺 Australia | 1,830 |
| 16 | 🇹🇷 Türkiye, Republic of | 1,570 |
| 17 | 🇮🇩 Indonesia | 1,440 |
| 18 | 🇳🇱 Netherlands | 1,320 |
| 19 | 🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia | 1,270 |
| 20 | 🇵🇱 Poland | 1,040 |
| 21 | 🇨🇭 Switzerland | 1,000 |
| 22 | 🇹🇼 Taiwan Province of China | 884.39 |
| 23 | 🇧🇪 Belgium | 716.98 |
| 24 | 🇮🇪 Ireland | 708.77 |
| 25 | 🇦🇷 Argentina | 683.37 |
| 26 | 🇸🇪 Sweden | 662.32 |
| 27 | 🇮🇱 Israel | 610.75 |
| 28 | 🇸🇬 Singapore | 574.18 |
| 29 | 🇦🇪 United Arab Emirates | 569.1 |
| 30 | 🇦🇹 Austria | 566.46 |
| 31 | 🇹🇭 Thailand | 558.57 |
| 32 | 🇳🇴 Norway | 517.1 |
| 33 | 🇵🇭 Philippines | 494.16 |
| 34 | 🇻🇳 Vietnam | 484.73 |
| 35 | 🇧🇩 Bangladesh | 475.01 |
| 36 | 🇲🇾 Malaysia | 470.57 |
| 37 | 🇩🇰 Denmark | 459.61 |
| 38 | 🇨🇴 Colombia | 438.12 |
| 39 | 🇭🇰 Hong Kong SAR | 428.23 |
| 40 | 🇿🇦 South Africa | 426.38 |
| 41 | 🇷🇴 Romania | 422.51 |
| 42 | 🇵🇰 Pakistan | 410.5 |
| 43 | 🇨🇿 Czech Republic | 383.38 |
| 44 | 🇮🇷 Iran | 356.51 |
| 45 | 🇪🇬 Egypt | 349.26 |
| 46 | 🇨🇱 Chile | 347.17 |
| 47 | 🇵🇹 Portugal | 337.94 |
| 48 | 🇵🇪 Peru | 318.48 |
| 49 | 🇫🇮 Finland | 314.72 |
| 50 | 🇰🇿 Kazakhstan | 300.05 |
| 51 | 🇩🇿 Algeria | 288.01 |
| 52 | 🇳🇬 Nigeria | 285 |
| 53 | 🇬🇷 Greece | 282.02 |
| 54 | 🇮🇶 Iraq | 265.46 |
| 55 | 🇳🇿 New Zealand | 262.91 |
| 56 | 🇭🇺 Hungary | 247.76 |
| 57 | 🇶🇦 Qatar | 222.12 |
| 58 | 🇺🇦 Ukraine | 209.71 |
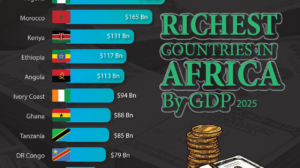
| 59 | 🇲🇦 Morocco | 179.61 |
| 60 | 🇰🇼 Kuwait | 157.47 |
| 61 | 🇸🇰 Slovak Republic | 154.59 |
| 62 | 🇺🇿 Uzbekistan | 137.48 |
| 63 | 🇰🇪 Kenya | 136.01 |
| 64 | 🇪🇨 Ecuador | 130.53 |
| 65 | 🇩🇴 Dominican Republic | 129.75 |
| 66 | 🇧🇬 Bulgaria | 127.92 |
| 67 | 🇵🇷 Puerto Rico | 126.55 |
| 68 | 🇬🇹 Guatemala | 120.85 |
| 69 | 🇦🇴 Angola | 115.17 |
| 70 | 🇬🇭 Ghana | 111.96 |
| 71 | 🇪🇹 Ethiopia | 109.49 |
| 72 | 🇴🇲 Oman | 105.19 |
| 73 | 🇭🇷 Croatia | 103.9 |
| 74 | 🇨🇷 Costa Rica | 102.64 |
| 75 | 🇱🇺 Luxembourg | 100.64 |
| 76 | 🇷🇸 Serbia | 100.05 |
| 77 | 🇨🇮 Côte d’Ivoire | 99.21 |
| 78 | 🇱🇹 Lithuania | 95.27 |
| 79 | 🇵🇦 Panama | 90.41 |
| 80 | 🇹🇿 Tanzania | 87.44 |
| 81 | 🇧🇾 Belarus | 85.74 |
| 82 | 🇺🇾 Uruguay | 84.99 |
| 83 | 🇻🇪 Venezuela | 82.77 |
| 84 | 🇨🇩 Congo, Dem. Rep. of the | 82.26 |
| 85 | 🇸🇮 Slovenia | 79.22 |
| 86 | 🇦🇿 Azerbaijan | 76.39 |
| 87 | 🇹🇲 Turkmenistan | 72.12 |
| 88 | 🇺🇬 Uganda | 64.99 |
| 89 | 🇨🇲 Cameroon | 60.58 |
| 90 | 🇲🇲 Myanmar | 60.56 |
| 91 | 🇹🇳 Tunisia | 59.07 |
| 92 | 🇧🇴 Bolivia | 57.09 |
| 93 | 🇯🇴 Jordan | 56.16 |
| 94 | 🇿🇼 Zimbabwe | 53.31 |
| 95 | 🇲🇴 Macao SAR | 52.38 |
| 96 | 🇰🇭 Cambodia | 48.8 |
| 97 | 🇱🇾 Libya | 47.94 |
| 98 | 🇱🇻 Latvia | 47.88 |
| 99 | 🇵🇾 Paraguay | 47.4 |
| 100 | 🇧🇭 Bahrain | 47.39 |
The data is sourced from the International Monetary Fund (IMF).
🇺🇸 United States
The United States remains the world’s largest economy with a GDP of around US $30.6 trillion in 2026. By 2030 it is likely to remain the world’s largest economy with projected GDP of around $36 trillion. The country’s huge population, wide customer market, and sectors like technology, finance, services, and consumer spending makes its economy the largest in the world.
The U.S. economy is still growing, but not as fast as it used to in past decades. Even with this slower growth, the United States remains one of the strongest economies in the world. This is mainly because America is strength lies in innovation and technologies. Additionally, US workers are highly productive, and the country has strong financial markets that help businesses get grow. All of these strengths help the U.S. stay ahead globally, even when its economic growth is only moderate.
However, the country is facing multiple challenges like large national debt, trade frictions with multiple countries especially with China, inequality, and global competition. As of late 2025, the total federal government debt of the U.S. has crossed $38 trillion. Recently under Donald J. Trump’s administration, the U.S. re‑imposed steep tariffs on many goods from countries like China.
🇨🇳 China
The China is the second largest economy in 2026, having a GDP of about $19.4 trillion. In the past few decades, China has been growing rapidly, shifting from an agriculture-based economy to one focused on industry and manufacturing. Today, the country also boasts of robust infrastructure, a growing services sector, and a large export market. Therefore, the country is expected to stay as the second largest economy by 2030, with a projected total GDP of $26 trillion.
China is an influential BRICS member as well as a key player in the Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO). Additionally, China is pursuing vital global initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative, where China builds roads, railways, ports, and other projects in many countries. The country is also involved in the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB), which provides loans for development projects across Asia.
Recently, China’s economic growth has slowed compared with its earlier double‑digit boom, but it is still expanding faster than most developed economies. At the same time, China is gradually trying to shift from export‑led growth to more domestic consumption and innovation.
Top 10 Largest Economies by GDP (PPP) in 2025
🇩🇪 Germany
The Germany is Europe’s largest economy and holds the third spot globally with a GDP of about US $5.01 trillion. Germany is known for making cars, machines, chemicals, and many high-quality manufactured goods. That manufacturing strength, along with massive exports give Germany a powerful economic edge around the world. It is home to world-renowned brands like Mercedes-Benz, BMW, and Siemens.
Economic growth in Germany has been slow recently. This is mostly because worldwide demand for goods has weakened, energy costs in Europe have gone up, and some important German industries are no longer growing as fast as they used to.
Even with these challenges, Germany’s economy is still strong and steady. It has reliable institutions, a highly skilled workforce, and long-standing export ties with many nations.
🇮🇳 India
With a GDP around $4.13 trillion, India is the fourth largest economy in the world. Over the last several years, India has grown steadily. Strong demand from within the country and vast expansions of key sectors, including services, technology, and exports, have contributed to its growth. Currently, the country’s economy is growing at about 6.5% a year, which is quite fast. In fact, the International Monetary Fund described India as the fastest-growing major economy among emerging markets.
India has the largest population globally and its young and growing population play a key role in its economy and growth potential. A large portion of India’s people are under 35, which gives the country what economists call a “demographic advantage.”
However, India is also faces challenges such as infrastructure needs, inequality, and the need to provide jobs and services for hundreds of millions. Though many young people are entering the workforce, many remain without stable, good-quality jobs.
🇯🇵 Japan
The Japan economy is among the world’s fifth-largest, at around US $4.28 trillion. It is a global leader in industries like electronics, automotive, and robotics. Renowned brands like Toyota, Honda, and Sony are integral to the country’s economic growth and development. But Japan’s growth is slow compared with emerging economies, partly because of an aging population, lower birth‑rate, and long‑term structural issues.
Japan is facing one of the worst demographic challenges in the world. The country’s population is shrinking. In 2026, births dropped to a record low, while deaths rose, meaning more people are dying than being born. Additionally, the working-age population (people roughly 15–64) has shrunk sharply compared with past decades. Because of this demographic shift, Japan’s economy has weakened compared to its old fast‑growth days.
🇬🇧 United Kingdom
The UK is among the world’s top economies in 2026, with its GDP of about $3.96 trillion. Its economy consists of a number of different sectors, including services such as finance, banking, and insurance, manufacturing, and international trade.
However, as in many other developed countries, the UK is facing some challenges: global economic uncertainty, higher inflation, and a rise in living costs. Notwithstanding these challenges, the UK remains one of the critical and diversified economies in Europe and the world.
🇫🇷 France
With a GDP of about $3.36 trillion, France is one of the major economies in Europe and in the world. Its economy encompasses a wide range of industries, including services, manufacturing, and agriculture. France’s economic growth has been steady in recent years but not very fast compared with some rapidly growing countries. Long-term challenges include an aging population, high public debt, and the need for structural reforms.
🇮🇹 Italy
Italy has a GDP of about $2.54 trillion in 2026 and is among the top 10 economies in the world. Its economy depends on industries such as manufacturing, exports, and tourism.
However, Italy faces serious long-term challenges, with its future being unclear. The country maintains large public debt, which is more than 130% of its GDP. It means that a big share of government revenue goes just to service that debt. The country’s population is also aging, and thus the working-age population is shrinking, meaning that fewer workers produce goods and services. Productivity growth is also weak, and many parts of the economy struggle to modernize.
🇷🇺 Russia
Russia remains a major economy by global ranking. Its economic strength largely comes from natural resources — oil, gas, minerals and other commodities — and exports of these resources have historically given Russia big revenues and global significance. Because of its large territory, resources, and export capacity, Russia stays among the world’s top ten larger economies.
However, heavy dependence on resource exports and less emphasis on diversified manufacturing or services, can limit Russia’s long‑term stability and growth.
🇨🇦 Canada
Canada is among the top 10 economies in the world, running at an approximate GDP of $2.28 trillion. Its economy grows through a combination of rich natural resources—such as oil, minerals, and agriculture—with strong service industries. This helps Canada to maintain steady growth and makes the economy more stable compared to many fast-changing or more volatile economies. But much of Canada’s growth depends on global demand for its exports, particularly natural resources. If global demand slows down or prices fall, that hits Canada hard.
Conclusion
The largest economies in the world have the highest GDPs, which means they produce the most goods and services. These countries play a key role in driving global trade, innovation, and shaping the future of the world economy. However, they also face major challenges such as income inequality and environmental challenges. Many of these countries also struggle with rising high debt burdens, inflation, and job market changes due to technology and globalization.





















Add Comment